Building A Doing Organization
 Doing Organisations (DOs) are inventive organs of next generations. Today technology empowers organizations to do more with less effort and transfer experience online with its stakeholders. DOs are powered with fitting technologies to network its business and decisionmaking processes with the support of TDF talents; thinking, doing and finishing. Modern DOs are broadly branded with six major
Doing Organisations (DOs) are inventive organs of next generations. Today technology empowers organizations to do more with less effort and transfer experience online with its stakeholders. DOs are powered with fitting technologies to network its business and decisionmaking processes with the support of TDF talents; thinking, doing and finishing. Modern DOs are broadly branded with six major
characteristics:
- Fatless
- Learner Interface (LI)
- Paperless
- Flatarchy and Networked
- Multi-Skilled
- Autonomated
Fatless
Fatless organizations are doing more with less. It is one of the most critical characteristics of DOs. In fact, less is more defined as “VALUE”. Invariably, it is fat that inhibits both speed and volume of outputs. A fat organization can be converted to a fatless or a lean by shredding its fats attached to processes. Some of the major types of resources that are treated as fats include space, material, machine and people. Hence, fatless organizations are characterized by less people, less machines, less space and less material consumption. DOs are being operated with vibrant and flexible set of fatless value chains.
Learner Interface (LI)
 In DOs, knowledge is being created in the organization and the same is open to its stakeholders at varying degrees based on needs for different layers of the organization. New ideas are essential if learning is to take place. Ideas and solutions are created online. In DOs, Managers are networked with people in the front office or shop floors. Research says, in the absence of a fully networked learning interface, more than 90% customer’s knowledge lies in the hands of operators whereas managers and CEOs possess only 9 % and 4% respectively. Hence, it is a dire need to develop a mega speed information flow from bottom to top if organizations need to learn from its own body of knowledge. It is the learner interface, which eliminates the real filtering effect (barriers of communication) of decisions and information throughout the organization.
In DOs, knowledge is being created in the organization and the same is open to its stakeholders at varying degrees based on needs for different layers of the organization. New ideas are essential if learning is to take place. Ideas and solutions are created online. In DOs, Managers are networked with people in the front office or shop floors. Research says, in the absence of a fully networked learning interface, more than 90% customer’s knowledge lies in the hands of operators whereas managers and CEOs possess only 9 % and 4% respectively. Hence, it is a dire need to develop a mega speed information flow from bottom to top if organizations need to learn from its own body of knowledge. It is the learner interface, which eliminates the real filtering effect (barriers of communication) of decisions and information throughout the organization.
Paperless
A paperless work environment is a workplace in which use of paper is eliminated or greatly reduced. This is done by converting documents and other papers in to digital form, a process known as digitization. This exercise not only reduces cost but also makes a green environment and increases the speed of decision making at all levels. What is crucial is to address compliance concerns with the support of legal and finance units.
Flatarchy and Networked
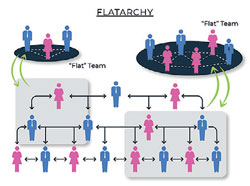 Flatarchies are organizations that are relatively flat yet can create an ad hoc hierarchy to work on a project or function and disband. Making real time decisions, doing, finishing them on time are fundamental to make DOs. Delegating decision-making powers to all layers, including operational level, is important to improve customer satisfaction and speed of doing business. Delegation and empowerment are effective only if TDF talents are recruited and employed. Then all employees can be digitally connected with a flat structure where hierarchy is no longer valued. Highly empowered TDF talents are the solution to make Dos of which the structure is always flat and interacted.
Flatarchies are organizations that are relatively flat yet can create an ad hoc hierarchy to work on a project or function and disband. Making real time decisions, doing, finishing them on time are fundamental to make DOs. Delegating decision-making powers to all layers, including operational level, is important to improve customer satisfaction and speed of doing business. Delegation and empowerment are effective only if TDF talents are recruited and employed. Then all employees can be digitally connected with a flat structure where hierarchy is no longer valued. Highly empowered TDF talents are the solution to make Dos of which the structure is always flat and interacted.
Multi-Skilled
Multi skilled actually refers to endowing multiple skills to single employees. Hiring multi-skilled TDF talents who are specialized in key operations facilitates making DOs. Multi skilled employees have number of different skills, enabling them to do more than one kind of operation with certain amount of adaptability. The challenge is how to develop multiskilled, as they are very much limited in the world of HR.
Autonomated
Major business processes of DOs are autonomated where people are theoretically divorced from machines and digital operating systems. Autonomated systems are designed in such a way that system itself finds defects and correct errors without support of people. This makes high quality perfect products with super speed and higher profits.
Building a Doing Organization
Learning something new or best practices does not make value addition or impact on bottom-line if it is not wisely executed. DOs are where execution demands the top priority and doers are ranked as key flyers. Doing is not a distinctive activity. It is of behaving, indeed a way of being, in which everyone is a great doer. DOs are made up of a set of fatless value chains. Developing competencies of people is the key to build a Doing Organization. Given below are the areas where competencies need to be developed to innovate new processes, so, that they make operations, easier, faster, cheaper and better. Six Sigma thinking, Lean thinking, Design thinking and thinking of Bloom’s taxonomy are the models being theorized to design DOs.
Six-Sigma has been practiced for years after being conceptualized in Motorola whereas lean thinking was born in Toyota and applied throughout the world. Bloom’s Taxonomy was created in 1956 under the leadership of educational psychologist, Dr. Benjamin Bloom in order to promote higher forms of thinking such as analyzing and evaluating concepts, processes, procedures, and principles. Nobel Prize winner, Herbert Simon, outlined one of the first formal models of the Design Thinking process. Simon’s model consists of seven major stages, each with component stages and activities, and was largely influential in shaping some of the most widely used Design Thinking process models today.
Innovation can be of three forms; namely product, process or business model innovation. DO is a business model. TDF model can be used in product, Process and business model innovation. Process of making a DO is explained below based on TDF model. In fact, TDFCertified Managers are involved in implementing design thinking process, so that, exponential growth in innovation can be experienced in DOs Design Thinking is a design methodology that provides a solution- based approach to solving problems. The Author has incorporated TDF model to indicate that process of designing is not a one -way but a process of continuous revisits until the product is tested in the market.
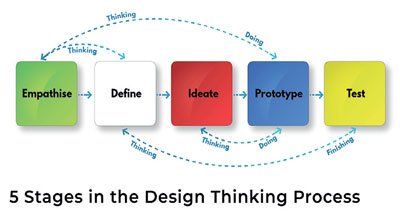
1. Empathise - Concept Generation
Concept is an idea or thought conceived in the mind. Conceiving is not enough; it has to be composed to produce desirable results in future. This is the key to growth and profits. But it does not happen in isolation, in a lab or in the executive suite. It comes from people who interact with customers. Employees hold all information and experience to explore new markets create new solutions and innovate from within. First step of making a profitable value chain is to be triggered with the mind-boggling exercise of loyal customers and employees to generate and conceptualize (generalized) an idea to begin with.
2. Define - Business Recipe Design
Business recipe design is a test of correlation between the output and inputs. It is worthwhile to test the correlation between output and input variables, so that production formula can be designed to enhance productivity. Finally, a statistical formula (recipe) can be designed to obtain highest possible outputs from selected few inputs which, strongly correlated with outputs. This process is called “making a Doing Algorithm”.
3. Ideate – Creating Solutions
During the third stage of the Design Thinking process, TDF designers are ready to start generating ideas. Once the doing algorithm is designed, and the problem is defined, alternative ways to create solutions are considered through brainstorming using SCAMPER technique. Form design refers to the physical appearance of a product (shape, colour, style etc) while functional design is concerned with how the product performs (usability, maintainability and reliability). Production design is concerned with how the product will be commercially made. Very often products are over designed or redesigned by Industrial Engineers. Late changes in design are both costly and disruptive. New approaches are simplification, standardization, modularity and design to manufacture. Modular cells are becoming popular in doing organizations.
4. Prototype Design
Prototype is a simulation or sample version of a final product, which, is used for testing prior to final launch. Lots of tools are available to make prototypes. Prototypes are one of the most important steps in the design process and the goal is to test products before sinking lots of time and money in to the final product. This step reveals areas where improvements are necessary and this can be done digitally or on a paper depending on requirements. The most accepted tool of Quality Policy Deployment (QFD), which translates voice of the customer in to technical design requirements, could be developed for further testing of the product with its competitors. QFD facilitates to upgrade the design based on the voice of customers and competitor analysis. This is one of the best tools being used by Doing Organizations to renew or innovate new products using the views of market trends. QFD is a must for each product of value chain.
5. Testing -Final Design and Process Plans
Designers or evaluators rigorously test the complete product using the best solutions identified during the prototyping phase. Once the prototype is tested, a pilot run of the process is conducted. Adjustments are made as needed before the final design is agreed on. Then, design specifications for the new product are considered. Final design consists of detailed drawings and specifications for the new product or service. Process plans include workable instructions and SOPs.
Digital Monitoring Dashboard
Process monitoring for continual improvement is the main purpose of designing a digital dashboard. In general, the dashboard includes the following input, process and output metrics to measure stability and capability of the value chain:
- First Pass Yield
- Defects Per Million Opportunities (DPMO)
- Run Chart for yield
- Control Charts
- Process Capability Index (CPk)
- OEE
Dashboard is vital to monitor online and daily performance of DOs as it facilitates and drives the basic principle of DOs; the doing principle of “walk the talk”.
For your feedback: [email protected]








































.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
