Digital Transformation and AI for brands strategy
 Digital transformation is currently one of the most talked-about business topics—possibly "the hottest"— on the corporate agenda. In actuality, neither the domains of corporate environment intervention nor the fundamental elements of digital transformation have been well defined as of yet. It's a process that begins with digitisation, which then leads to digitalisation, which opens the door for a company or brand to undergo digital transformation. Digitalisation is not just about technology.
Digital transformation is currently one of the most talked-about business topics—possibly "the hottest"— on the corporate agenda. In actuality, neither the domains of corporate environment intervention nor the fundamental elements of digital transformation have been well defined as of yet. It's a process that begins with digitisation, which then leads to digitalisation, which opens the door for a company or brand to undergo digital transformation. Digitalisation is not just about technology.
 Digitisation vs digitalisation
Digitisation vs digitalisation
The process of transforming data from a physical format into a digital one is called digitisation. It is essentially the first stage of a more thorough digital transformation. This could entail turning analogue material, such pictures and audio recordings, into digital files or scanning paper documents to produce digital copies.
• Preservation of original documents
• Easy sharing and distribution
• Reduction in physical storage space
The primary goal of digitisation is to make information more accessible and easier to manage. However, it's important to note that digitisation alone does not change how the information is used—it simply changes its format. Digitalisation refers to the use of digital technologies to change a business model and provide new revenue and value- producing opportunities. It is the process of moving to a digital business. Digitalisation transforms the way businesses operate, integrating digital technology into all areas, and fundamentally changing how they deliver value to customers. It's not just about automating or inserting technology into an existing process, but about rethinking and redesigning these processes to be digital-first.
• Process optimisation is often the first step in digitalisation.
• Enhancing customer interaction and engagement through digital channels.
• Utilising data analytics for informed decision-making.
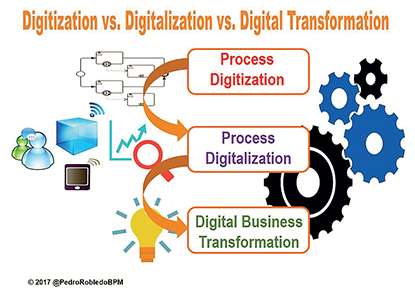 Process Digitisation:
Process Digitisation:
Transform a process into a digital format that can either replicate the process exactly as it is (AS-IS) or enhance what is currently being done by adding process optimisation. Companies frequently claim to have been "digitised" (also known as "digitisation"), arguing that they have reduced or eliminated nearly all of their paper records (digitally storing the information) and that they have replaced manual processes with digital models of processes represented under BPMN notation, or Business Process Model & Notation. These models have even been able to automate manual processes that are based on paper and can be carried out with vertical applications that solve the task chain, or they have even been able to choose (more successfully) to use a BPM: Workflow engine (Business Process Management) that manages the process to perform a complete orchestration of all process flows. This Digitisation is a good start, but it is not a Process Digitalisation nor a Digital Transformation.
Process Digitalisation:
In order to transform processes— not just digitisation—into ones that are more productive, profitable, efficient, and satisfy customers in both their digital and physical interactions with the business, digitalisation entails the use of certain digital technologies in the processes and the digital management of data (digitised and digitally native data). As a result, digitalisation makes it possible to leverage digital data to improve business outcomes, generate new income, reduce expenses, and improve customer experiences—all of which add significant value when utilising digital technologies.
Digital Business Transformation:
Using digital technologies to create new business designs is the key to doing things differently. In order to optimise the current value chain, digitalisation involves more than just automating or integrating technology into an existing process. It also involves altering the business model, changing the value chain, and undoubtedly producing a new supply of goods and services (due to the use or integration of digital technologies in the goods or services before the transformation), which results in a better and new method of offering value to customers. Additionally, they will necessitate the development of new critical processes required for the new business model, as well as the modernisation, simplification, and rationalisation of the current business processes.
Benefits for Brands and Branding
As a result, it is evident that both digitisation and digitalisation are beneficial to brands and branding. Because digitalisation enables brands to boost do-it-yourself (DOI) and decrease human involvement, it enables them to standardise their service delivery procedures. For instance, more transactions may be made online when online banking is marketed as part of the digital transformation, which lowers the number of people visiting the branch network and, thus, makes life easier for the banking employees. There are numerous drawbacks to this, though, as some clients prefer a human touch to a chatbot when they have questions answered.
Additionally, the use of internet banking is contributing to an increase in scams in the current environment. But it’s visible on the streets of India how the micro vendors who sell fruits on the street are making use of QR codes to collect money from the customers. Additionally, India has taken efforts to do away with the requirement for passwords for online transactions involving lower amounts. Additionally, this has increased the use of online banking. Because we are restricting these possibilities, we are preventing small vendors in Sri Lanka from taking use of these advantages, which limits many facets of digital access.
Artificial Intelligence and the Role of AI
Artificial intelligence is one of the core technologies in digital transformation that is helping businesses scale up. In fact, according to the latest report by Research and Markets, AI is expected to achieve a compound annual growth rate of 52% by 2025, indicating its rapid adoption by global businesses. AI is now being integrated into and deployed across a variety of sectors, such as national security, healthcare, logistics, and education. In the next article let’s discuss the role of AI in digital transformation.








































.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
